“Vibration” Numerical Problems
Try to solve the following “vibration” numerical problems to clear the concepts in solving the numerical problems.
First of all go to the theory portion of the respective topic and then try to solve the numerical problems by yourself. If facing problem in solving the numerical, click on the Go to solution button to see the ready made solution placed at the bottom of each numerical problem.
01. PROBLEM – P060101
The following figures depict two circular motions. The radius of the circle, the period of revolution, the initial position and the sense of rotation are indicated on the figure.
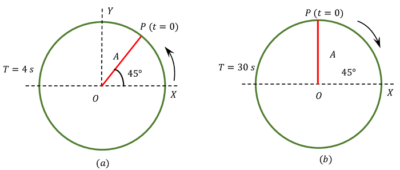
Obtain the SHM equations of the ( x ) projection of the radius vector of rotating particle P .
Keywords related to this problem.
02. PROBLEM – P060102
A particle execute SHM with a time period of ( 2 \ s ) and amplitude ( 5 \ cm ) . Find (1) displacement (2) velocity (3) acceleration after \left ( \frac {1}{3} \ s \right ) starting from the mean position.
Keywords related to this problem.
- Displacement in simple harmonic motion.
- Velocity in simple harmonic motion.
- Acceleration in simple harmonic motion.
03. PROBLEM – P060103
A particle is executing SHM . Initially the particle is at origin and it covers distance from ( 0 ) to ( A/2 ) in time ( t_1 ) and from ( A/2 ) to ( A ) in time ( t_2 ) . Find the ratio \left ( \frac {t_2}{t_1} \right ) .
Keywords related to this problem.
04. PROBLEM – P060104
A particle is executing SHM along a straight line has a velocity of ( 4 \ m/s ) when at a distance ( 3 \ m ) from the mean position and ( 3 \ m/s ) when at a distance of ( 4 \ m ) from it. Find the time it takes to travel ( 2.5 \ m ) from the positive extreme end.
Keywords related to this problem.
- Displacement in simple harmonic motion.
- Velocity in simple harmonic motion.
- Time period in simple harmonic motion.
05. PROBLEM – P060105
A particle is executing SHM of amplitude ( A ) . (1) at what distance from the mean position is its kinetic energy equal to its potential energy? (2) at what point is its speed is half of the maximum speed?
Keywords related to this problem.
06. PROBLEM – P060106
A spring compressed by ( 0.2 \ m ) develops a restoring force ( 25 \ N ) . A body of mass ( 5 \ kg ) is placed over it. Deduce (1) force constant of the spring (2) the depression of the spring under the weight of the body and (3) the period of oscillations if the body is disturbed. Take ( g = 10 \ N/kg ) .
Keywords related to this problem.
07. PROBLEM – P060107
Two masses ( m_1 ) and ( m_2 ) are suspended together by a mass less spring of force constant ( k = 12.5 \ N/m ) as shown in figure. When they are in equilibrium position, mass ( m_1 ) is gently removed.
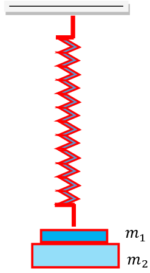
Calculate the angular frequency and the amplitude of oscillations of ( m_2 ) . Given ( g = 10 \ m \ s^{-2} )
Keywords related to this problem.
08. PROBLEM – P060108
A trolley of mass ( 3.0 \ kg ) is connected to two identical springs each of force constant ( 600 \ N/m ) as shown in figure.
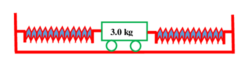
If the trolley is displaced from its equilibrium position by ( 5.0 \ cm ) and released, what is (1) the period of ensuing oscillations? (2) The maximum speed of trolley (3) How much is the total energy dissipated as heat by the time the trolley comes to rest due to dissipating forces?
Keywords related to this problem.
09. PROBLEM – P060109
Two identical springs have the same force constants of ( 147 N/m ) . What elongation will be produced in each spring in each case as shown in figure? Take ( g = 9.8 \ m \ s^{-2} )
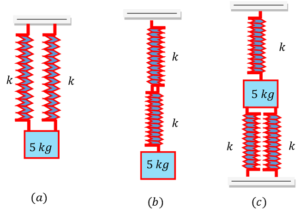
Keywords related to this problem.
10. PROBLEM – P060110
A sphere is hung with a wire. The 30 \degree rotation of the sphere about the wire generates a rotating torque of ( 4.6 \ N \ m ) . If the moment of inertia of the sphere is ( I = 0.082 \ kg \ m^2 ) , deduce the frequency of angular oscillations.
Keywords related to this problem.
11. PROBLEM – P060111
A copper wire is held at the two ends by rigid supports. At 30 \degree C , the wire is just taut with negligible tension. Find the speed of transverse waves in the wire at 10 \degree C . Given ( \alpha = 1.7 \times 10^5 \degree C ), \ ( \gamma = 104 \times 10^{11} \ N \ m^{-2} ) and ( \rho = 9 \times 10^3 \ kg \ m^{-3} )
Keywords related to this problem.
12. PROBLEM – P060112
A harmonically moving transverse wave on a string has a maximum particle velocity and acceleration of ( 3 \ m \ s^{-1} ) and ( 90 \ m \ s^{-1} ) respectively. Velocity of the wave is ( 20 \ m \ s^{-1} ) .
Find the wave form.
Keywords related to this problem.
13. PROBLEM – P060113
The equation of a plane progressive wave is \left [ y = 10 \sin 2 \pi \left ( t - 0.005 x \right ) \right ] where ( y ) and ( x ) are in cm and ( t ) is in seconds.
Calculate the amplitude, frequency, wavelength and velocity of the wave.
Keywords related to this problem.
14. PROBLEM – P060114
For the plane wave represented by \left [ y = 2.5 \times 10^{-0.02x} \cos \left ( 800 t - 0.82 x + \frac {\pi}{2} \right ) \right ] write down –
- The general expression for phase ( \phi ) .
- The phase at ( x = 0 ) and ( t = 0 ) .
- The phase difference between the points separated by ( 20 \ cm ) along X axis.
- The change in phase at a given place in ( 0.6 ) milliseconds and (5) the amplitude at ( x = 100 \ m ) .
Take units of ( y ), \ ( t ) \ \& \ ( x ) as ( 10^{-5} cm ), \ ( s ) \ \& \ ( m ) respectively.
Keywords related to this problem.
15. PROBLEM – P060115
Find the temperature at which sound travels in hydrogen with the same velocity as in oxygen at 1000 \degree C . Density of oxygen is ( 16 ) times that of hydrogen.
Keywords related to this problem.
16. PROBLEM – P060116
A gas is a mixture of two parts by volume of hydrogen and one part by volume of nitrogen. If the velocity of sound in hydrogen at 0 \degree C is ( 1300 \ m/s ) , find the velocity of sound in the gaseous mixture at 27 \degree C .
Keywords related to this problem.
17. PROBLEM – P060117
A wire having linear mass density of ( 50 \times 10^{-3} \ kg \ m^{-1} ) is stretched between two rigid supports with a tension of ( 450 \ N ) . The wire resonates at a frequency of ( 420 \ Hz ) . The next higher frequency at which the same wire resonates is ( 490 \ Hz ) . Find the length of the wire.
Keywords related to this problem.
18. PROBLEM – P060118
A pipe ( 30.0 \ cm ) long is open at both ends. Which harmonic mode of the pipe is resonantly excited by a ( 1.1 \ kHz ) source? Will resonance with the same source be observed if one end of the pipe is closed? Take the speed of the sound in air as ( 330 \ m \ s^{-1} )
Keywords related to this problem.
19. PROBLEM – P060119
When two tuning forks, fork 1 and fork 2 are sounded simultaneously, 4 beats per second are heard. Now some tape is attached on the prong of the fork 2. When the tuning forks are sounded again, 6 beats per second are heard. If the frequency of fork 1 is ( 200 \ Hz ) , then what was the original frequency of fork 2?
Keywords related to this problem.
20. PROBLEM – P060120
An observer standing on railway gateway receives frequencies of ( 2.2 \ kHz ) and ( 1.8 \ kHz ) when the train approaches and recedes from the observer. Find the velocity of the train. The speed of sound in air is ( 300 \ m-s^{-1} ) .
Keywords related to this problem.
