How Sound Waves propagate?
Sound wave are wave motion which travels through a medium due to vibrations of medium particles about their mean position.
All properties of wave motion are applicable to motion of sound waves. A medium is compulsory for propagation of sound waves.
Humans and other creatures use sound waves to communicate with each other and also to perform various tasks. Our vocal chords generate sound waves which transmitted through the air to the ears of listener.
Modern communication technologies generate sound waves for communication to a mass of people such as Radio, Television, Amplifier, Siren etc.
Acoustics
Acoustics is the branch of science which deals with study of mechanical sound waves in gases, liquids and solids.
Application of acoustic is found in various disciplines like audio signal processing, architectural acoustic, environmental noise, musical acoustics, noise control, speech therapy, ultrasound testing, underwater acoustics etc.
Sonic Waves
Sound waves are also called sonic waves.
Sonic wave means acoustic waves which are capable to sense and analyze by human brain. Different animal species has different acoustic capabilities.
Based on frequency, sound waves are classified as –
- Infrasonic sound waves.
- Sonic sound waves.
- Ultrasonic sound waves.
Infrasonic Wave
Infrasonic waves are sound waves of frequency less than ( 20 \ Hz ) . These are not within the hearing range capacity for humans. Some animal species have abilities to hear them.
These waves are used for industrial purposes like (1) to locate the leakage in underground pipelines (2) to investigate the internal structure of planets etc.
Seismic waves produced during earthquake is an example of infrasonic waves.
Sonic Wave
Sonic waves are sound waves of frequency range in between ( 20 \ Hz ) \ \text {to} \ ( 20 \ kHz ) . These are within the hearing range capacity for humans.
Sonic waves are the means of communication between the creatures in this world.
Sound waves are used for many purposes like (1) communication by talking, television, radio, siren etc. (2) Hunting – locating a distant body by use of reflection method (3) Ocean exploration – use of echolocation to detect position of under water bodies, submarines etc. (4) detection of under ground resources (4) Musical instruments etc.
Ultrasonic Wave
Ultrasonic waves are sound waves of frequency above ( 20 \ kHz ) . These are again beyond the hearing range capacity for humans.
Ultrasonic waves have very wide application in science and technology like (1) used in transducers for detecting flaws and cavities in materials (2) cutting and machining of very hard materials (3) used in medical science to diagnose, examine of proper functioning or damages to internal body parts and treatment etc.
Types of Sound Waves
Based on the relationship between direction of motion of sound wave and direction of motion of vibrating medium particles, sound waves are broadly classified into two categories. These are as follows –
- Transverse sound waves.
- Longitudinal sound waves.
Transverse Sound Wave
In transverse sound wave, the medium particles vibrate perpendicular to the direction of propagation of sound wave.
Vibration of medium particles in transverse wave is shown in figure. Transverse wave of sound has following characteristics –
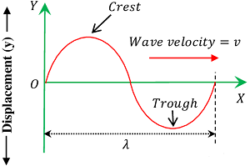
- Displacement of medium particles is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of sound wave.
- Transverse wave travels in the form of crests and troughs. Points of maximum displacement of medium particles forms crests ( i.e. point of maximum displacement in upward direction ) and troughs ( i.e. point of maximum displacement in downward direction ).
- One crest and one successive trough together constitute one complete cycle.
- Distance between top points of two successive crests or bottom points of two successive troughs is called wavelength.
- Transverse sound waves when travels involve changes in shape of medium.
- So, they can travel through a medium having shear modulus of rigidity such as solids.
- Transverse sound waves can not travel through liquids or gases because these mediums have no modulus of rigidity.
- Speed of sound depends upon modulus of rigidity ( \eta ) and density ( \rho ) .
Longitudinal Sound Wave
In longitudinal sound waves, medium particles vibrate parallel to the direction of propagation of sound.
Vibration of medium particles in a longitudinal wave is shown in figure. In longitudinal sound waves –
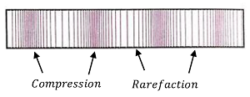
- Displacement of medium particles is parallel to the direction of propagation of sound.
- Longitudinal waves travel in the form of compression and rarefaction. Compression is the zone of high density of medium particles and rarefaction is the zone of lesser density of medium particles.
- One complete compression and one complete rarefaction together constitute one complete cycle of vibration.
- Distance between two similar points of two successive compression or rarefaction is called wavelength.
- Longitudinal sound waves travel and involve changes in volume and density of medium.
- So they can travel through a medium which can sustain compression stress such as solids, liquids and gases.
- Speed of sound depends upon bulk modulus ( k ) and density ( \rho ) .
